During a project, you may wonder “who does what,” “who is supposed to approve what,” or “who is responsible for what.” Indeed, without a clear definition of roles, tasks, and responsibilities, some people tend to shirk their duties in an organisational structure.
To prevent this situation, whether during a project or when defining a process, we use a simple and effective management tool: the RACI (or RASCI) matrix.
What is a RACI Matrix?
The RACI matrix is a management tool used to determine the roles and responsibilities of each stakeholder in a project or process. The name of the matrix (RACI) is an acronym where each letter corresponds to a specific responsibility :
- R: Responsible; in charge of performing the task
- A: Accountable; in charge of supervising the task and reporting to the hierarchy
- C: Consulted; in charge of contributing, providing advice
- I: Informed; must be informed
It is a two-dimensional table with :
- In rows: activities, tasks, actions, deliverables, etc.
- In columns: stakeholders, designated as individuals, organisational entities, functions, job titles, teams, etc.
In each cell of the RACI matrix, the role played by the stakeholder is noted according to the activity or task :
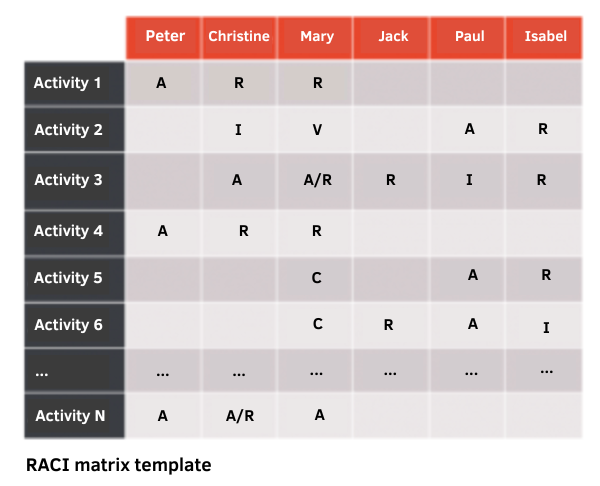
Note that some variants exist depending on whether the RACI matrix is used in English or French; therefore, it is important to be vigilant when using this management tool by systematically re-specifying the meaning of the letters. The most common French variant, for example, has reversed responsibilities between “A” and “R”:
- A: Autorité; sometimes accountable is perceived as “responsible”: person in charge of performing the action
- R: Responsable; meaning “accountable”: person in charge of supervising the action or task and reporting to the hierarchy
- C: Consulté; person in charge of contributing, providing advice
- I: Informé; person who must be informed

An invaluable tool

RACI or RASCI Matrix
Another variant of the RACI matrix exists: the RASCI matrix. The letter “S” stands for “Support” in English and also translates to “Support” in French. When the letter “S” is added, it designates the person who assists the responsible in completing the task.
What are the rules for using a RACI Matrix?
There are some rules to follow when creating a RACI matrix for a project within a team:
- Each activity or task must have at least one performer (R: Responsible).
- For a given activity, a stakeholder can simultaneously be a performer (R: Responsible) and an approver (A: Accountable).
- An activity can have only one approver (A: Accountable).
- The approver (A: Accountable) subcontracts to the performer(s) (R: Responsible), but remains responsible for the action: if the performer(s) (R: Responsible) do not meet their objectives, the approver (A: Accountable) assumes responsibility.
- Consulted stakeholders (C: Consulted) have no authority for the activity in question; it is always the approver (A: Accountable) who decides.
- Informed stakeholders (I: Informed) must be informed because they are impacted by the activity.
How to build a RACI or RASCI matrix for a project ?
The process for building a RACI or RASCI matrix is as follows :
- Identify the stakeholders of the project or process (e.g., the client, the project manager, the client, the production team, etc.).
- Define the activities/tasks/actions/deliverables produced or required for the successful completion of the project or process.
- Define the roles and responsibilities of the stakeholders for each activity (using the 4 letters: R, A, C, I; ensuring agreement on the definition of each letter).
Our added value
The RACI or RASCI matrix is a good management tool for a team as it allows for the implementation of quick-wins (most relevant improvements) in environments where roles and responsibilities of a project or process need to be quickly clarified (without wanting to go through an in-depth process mapping, functional organisational chart construction, job description overhaul, etc.).
We believe that special care should be taken in identifying activities, which often are not at the appropriate level (sometimes too broad or sometimes too specific). We also recommend paying particular attention to the holders of roles and responsibilities in project management, who are sometimes individuals, functions, bodies, or teams. When it involves a group of several people, you must be vigilant to ensure that responsibility is not diluted.
Finally, although the RACI or RASCI matrix facilitates project management by distributing responsibilities among stakeholders, it does not resolve team dysfunctions and will not make you more efficient. We invite you to consult our offer on organisational intelligence to go further in this regard.

A clear vision of each role in a project

4 important points on role clarity in a project and the RACI matrix
- Importance of role clarity in project management
The RACI matrix is an essential tool that provides a clear vision of roles and responsibilities within a project. In a professional environment where companies are constantly transforming, adapting and innovating, role clarity is crucial. The RACI matrix serves as a compass to guide teams, ensuring that each member knows exactly what they need to do, thus avoiding ambiguities and overlaps. - The four roles of matrix RACI : define to succeed
The RACI matrix breaks down into four key : Responsible, Accountable; Consulted and Informed. Each role has a specific meaning, ranging from task execution to consultation or information. Presented in a table format, this matrix allows for quick visualisation of responsibilities, facilitating communication and coordination within the team. - RACI : more than a tool, a catalyst for success
Beyond its structure, the RACI matrix offers numerous advantages. It eliminates ambiguities by clearly defining responsibilities, improves communication by identifying who needs to be consulted or informed at each step, and prevents conflicts by establishing clear boundaries between roles. By using the RACI matrix, companies can avoid duplications, omissions and ensure successful project completion. - Effective implementation and errors to avoid
Although beneficial, implementing the RACI matrix can present challenges. Common errors, such as role ambiguity or neglecting updates, can hinder its effectiveness. However, by following key advice, such as clarifying roles from the outset, widely consulting stakeholders, and regular reviews, companies can maximise the benefits of the matrix while minimising potential pitfalls.
Contact us
Write to usFollow us on LinkedIn
SuivreAller plus loin
Different types of organisational charts: definition and uses
Organisational chart: a visual tool for structuring and understanding an organisation...
Organisational structure: definition, advantages, and disadvantages of different business structures
Organisational structure: key to performance and adaptability. ...

